Difference between revisions of "Random Walk"
(add triangular images) |
(added images) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
=Random Walks in NetLogo= | =Random Walks in NetLogo= | ||
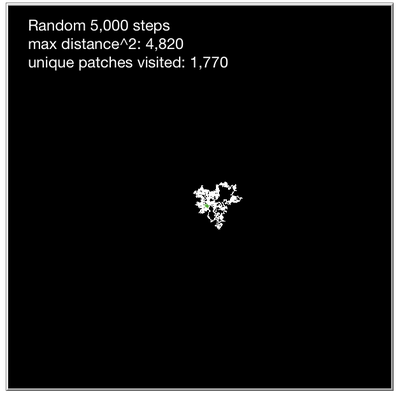
| + | Each tick, generate a random heading from 0-359. Gives an even distribution of headings, and the resulting random walk has lots of backtracing and crossings. | ||
rt random 360 | rt random 360 | ||
fd 1 | fd 1 | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File: random_walk.png|400px]] | ||
=Triangular Random Walk= | =Triangular Random Walk= | ||
| Line 14: | Line 17: | ||
Distribution: | Distribution: | ||
| − | [[File: triangular_heading.png]] [[File: triangular_walk.png]] | + | [[File: triangular_heading.png|400px]] [[File: triangular_walk.png|400px]] |
=Some Theory= | =Some Theory= | ||
| − | In a true random walk (ie Brownian motion) the mean displacement along the x-axis is proportional to the square root of time dx=sqrt (2Dt), which gives mean radius of a circle covered by the random walk | + | In a true random walk (ie Brownian motion) the mean displacement along the x-axis is proportional to the square root of time dx=sqrt (2Dt), where D is the diffusion constant which gives mean radius of a circle covered by the random walk |
Einstein, Albert (May 1905). [https://www.zbp.univie.ac.at/dokumente/einstein2.pdf "Über die von der molekularkinetischen Theorie der Wärme geforderte Bewegung von in ruhenden Flüssigkeiten suspendierten Teilchen" (PDF)]. Annalen der Physik (in German). 322 (8): 549–560. Bibcode:1905AnP...322..549E. doi:10.1002/andp.19053220806. Retrieved 2008-04-10. | Einstein, Albert (May 1905). [https://www.zbp.univie.ac.at/dokumente/einstein2.pdf "Über die von der molekularkinetischen Theorie der Wärme geforderte Bewegung von in ruhenden Flüssigkeiten suspendierten Teilchen" (PDF)]. Annalen der Physik (in German). 322 (8): 549–560. Bibcode:1905AnP...322..549E. doi:10.1002/andp.19053220806. Retrieved 2008-04-10. | ||
| Line 24: | Line 27: | ||
Einstein, Albert (1989). [https://einsteinpapers.press.princeton.edu/vol2-trans/137 "On the movement of small particles suspended in a stationary liquid demanded by the molecular-kinetic theory of heat" (PDF)]. Princeton University Press | Einstein, Albert (1989). [https://einsteinpapers.press.princeton.edu/vol2-trans/137 "On the movement of small particles suspended in a stationary liquid demanded by the molecular-kinetic theory of heat" (PDF)]. Princeton University Press | ||
| − | A random walk constrained on a lattice | + | A random walk constrained to 2 dimensions, the mean displacement is proportional to sqrt(t). |
| + | |||
| + | There are supposed to be interesting properties of random walk on a lattice, which is probably the best model of NetLogo movement. | ||
McCrea, W. H. and Whipple, F. J. W. "Random Paths in Two and Three Dimensions." Proc. Roy. Soc. Edinburgh 60, 281-298, 1940. | McCrea, W. H. and Whipple, F. J. W. "Random Paths in Two and Three Dimensions." Proc. Roy. Soc. Edinburgh 60, 281-298, 1940. | ||
Revision as of 18:53, 6 October 2019
Random Walks in NetLogo
Each tick, generate a random heading from 0-359. Gives an even distribution of headings, and the resulting random walk has lots of backtracing and crossings.
rt random 360 fd 1
Triangular Random Walk
Advance +/- 50 degrees from straight ahead, gives a triangular distribution around 0
rt random 50 lt random 50
Distribution:
Some Theory
In a true random walk (ie Brownian motion) the mean displacement along the x-axis is proportional to the square root of time dx=sqrt (2Dt), where D is the diffusion constant which gives mean radius of a circle covered by the random walk
Einstein, Albert (May 1905). "Über die von der molekularkinetischen Theorie der Wärme geforderte Bewegung von in ruhenden Flüssigkeiten suspendierten Teilchen" (PDF). Annalen der Physik (in German). 322 (8): 549–560. Bibcode:1905AnP...322..549E. doi:10.1002/andp.19053220806. Retrieved 2008-04-10.
Einstein, Albert (1989). "On the movement of small particles suspended in a stationary liquid demanded by the molecular-kinetic theory of heat" (PDF). Princeton University Press
A random walk constrained to 2 dimensions, the mean displacement is proportional to sqrt(t).
There are supposed to be interesting properties of random walk on a lattice, which is probably the best model of NetLogo movement.
McCrea, W. H. and Whipple, F. J. W. "Random Paths in Two and Three Dimensions." Proc. Roy. Soc. Edinburgh 60, 281-298, 1940.